Lecture-2
You can find the lecture video below:
Do not need to follow github.com as it is said in the video. You can follow the documentation when you watch the video on this webpage instead of GitHub.
Basic Terminal Commands on Ubuntu
Open a Terminal Window by
- pressing
Windows Keyand typingTerminal, - pressing
ctrl+alt+t, - or clicking the Terminal Icon on the left dock.
0. Use of terminal by the keyboard
You cannot use mouse on the terminal. But sometimes we can write a long command with a typo and need to go left and fix it. You can use
1- ctrl+b to go to the left letter by letter,
2- ctrl+a to go to the left-most first character,
3- ctrl+f to go to the right letter by letter,
4- ctrl+e to go to the right-most last character.
1. pwd
pwd stands for Print Work Directory in Linux.
Terminal opens at the home directory by default in Ubuntu.
If you type pwd and press Enter you will see your home directory.
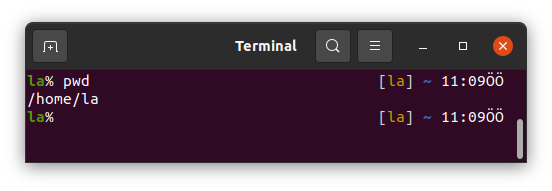
in my case.
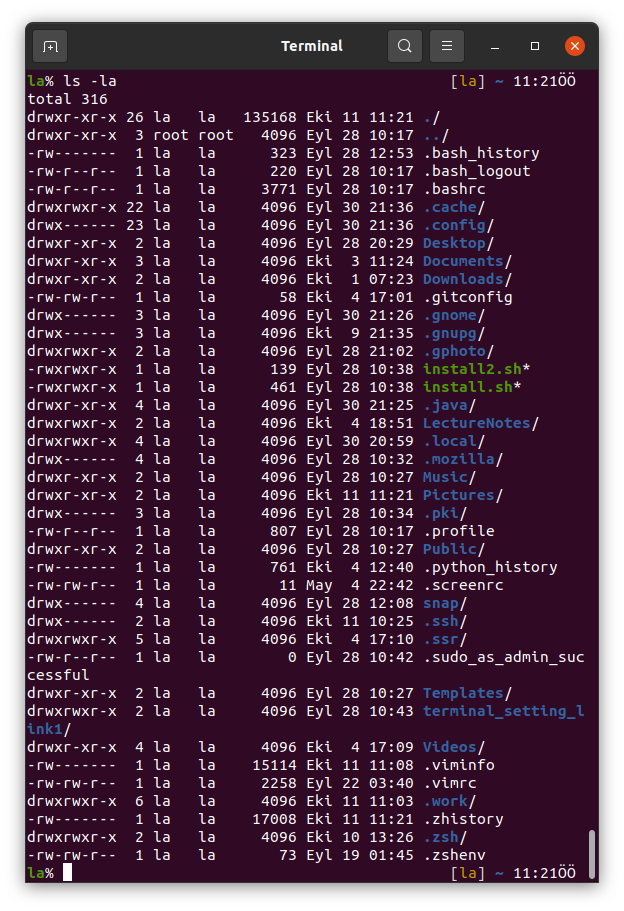
2. ls
We can list the files and folders in a directory using this command.
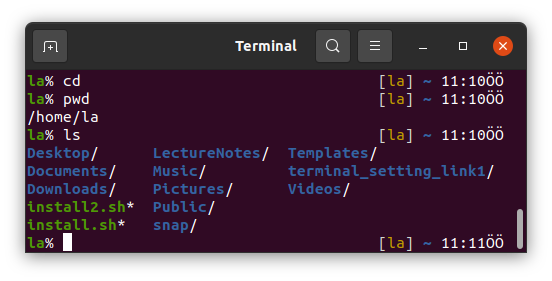
Shows the files and folders located in your /home/la directory.
You should see the same folders in your home directory
if you followed this repository to install Ubuntu on your computer or if you use one of our lab computers.
ls also has some options with it. One of them is ls -l which prints the details of the files such as the size of a file in KB and the date that the file has been created.
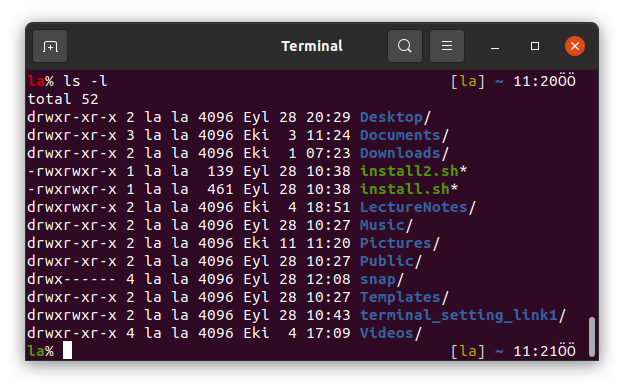
The other is ls -la and used for printing also the hidden files starting with . in your working directory.
3. cd
cd stands for Change Directory in Linux.
We can go to a directory using the cd command as shown below.
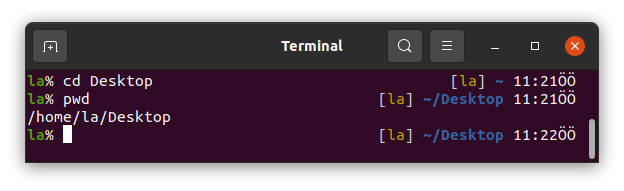
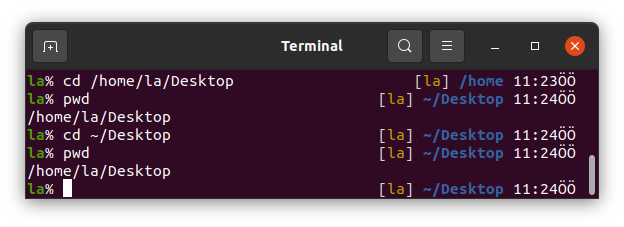
This usage of cd lets we go to a directory relatively your working directory.
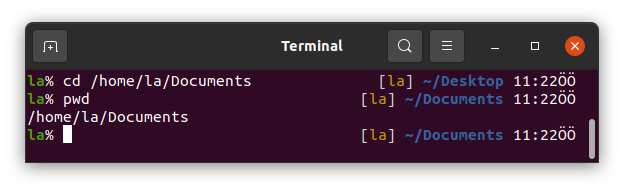
It can also be used as absolute path.
We can use cd alone in commandline to go to home directory.
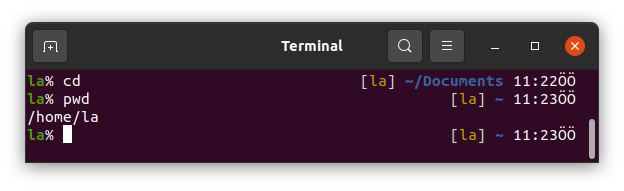
.. "two dots without space" is used to go an upper directory. Here we are in /home/la. Typing .. we can go to /home directory.
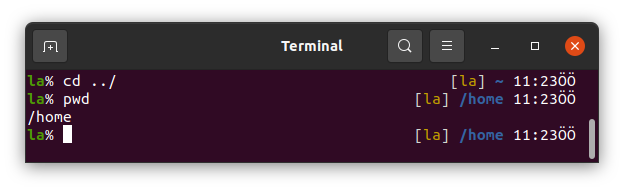
~ which is tilde is equal to /home/la in Linux Terminal.
4. mkdir
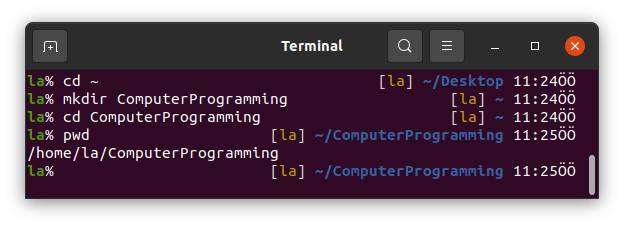
mkdir is the acronym of Make Directory.
We can make directories using this command.
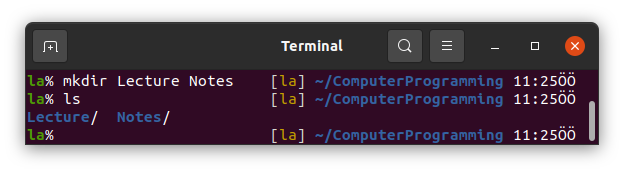
If we use space between two word when we make directories using mkdir it makes two different folders.
So, if we want to make a directory so called "Lecture Notes" we should type
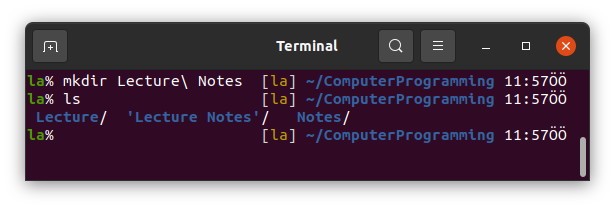
but this way is usually not preferred by Linux users. Instead we use Lecture_Notes or LectureNotes. For the differences you can read here.

If we need to make multiple directories, such as LectureNotes/Lecture1 we can use mkdir.
However, if any of the non-existing directories included in our command, we get an error.
To get rid of this error we should use -p option as follows.
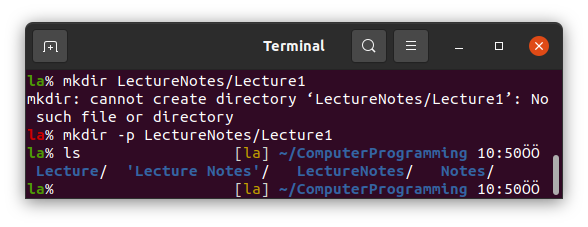
This will both make the LectureNotes directory and Lecture1 in it.
5. touch
This is a command creating files in Linux.
First go to the LectureNotes directory and follow the instructions.
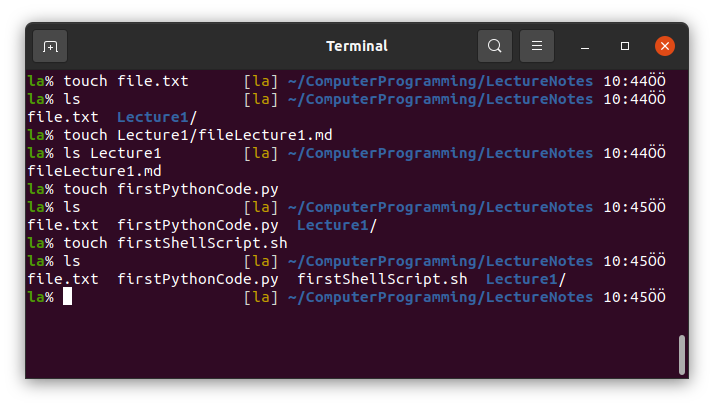
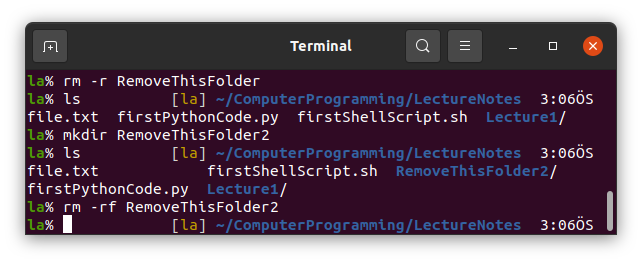
6. rm
rm removes files in Linux. But we cannor remove folders using rm alone.
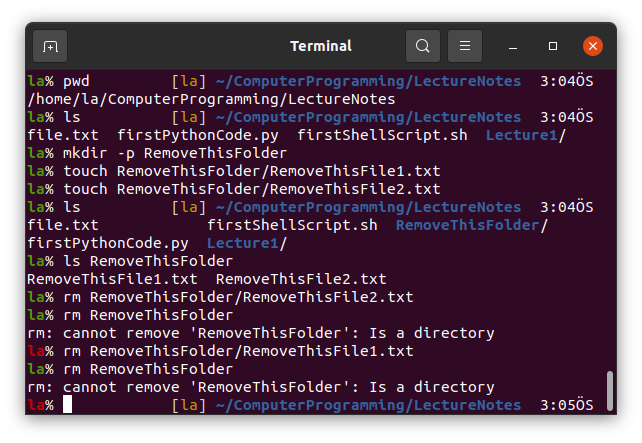
We need to use -r option to remove folders or -rf option so as not to get error for non-existing files and arguments.
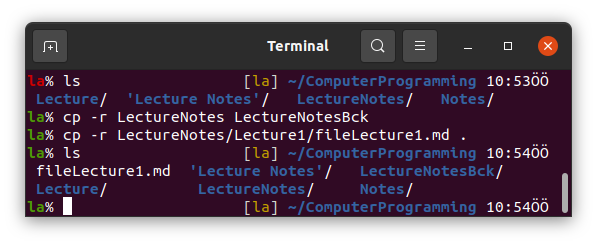
7. cp
cp is acronym of Copy in Linux Terminal. A -r option is used with cp for similar reasons.
8. ln -s
ln -s stands for Link. We can use this to link a file or folder to somewhere else.
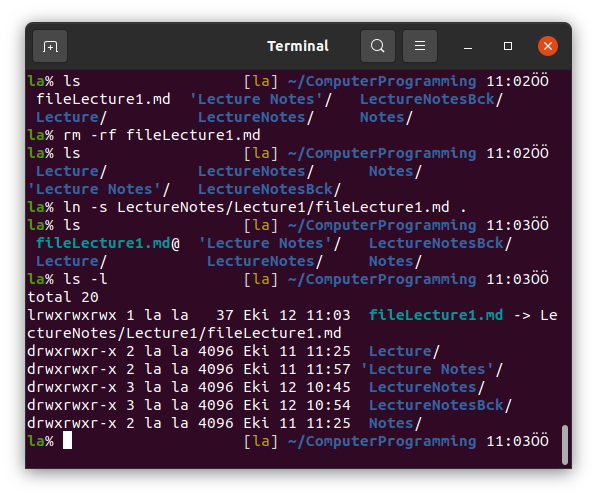
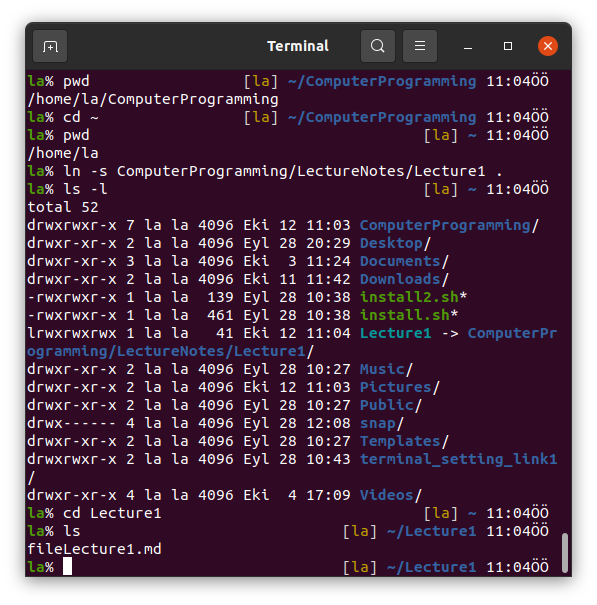
We can also link a folder.
9. mv
mv stands for move. We can move files and folders using mv.
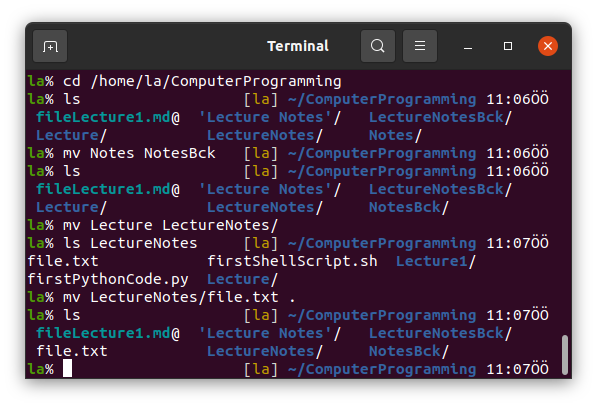
10. gedit
gedit is the command to open the Ubuntu's default text editor Gedit. We can open some files using it change and save.
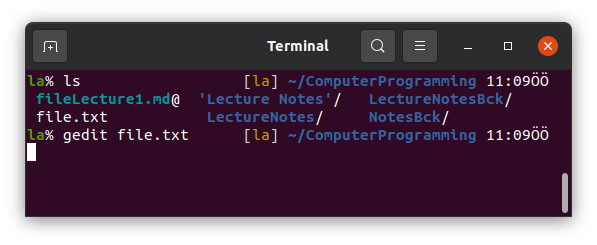
The file editor is opened immediately and you can write on it.
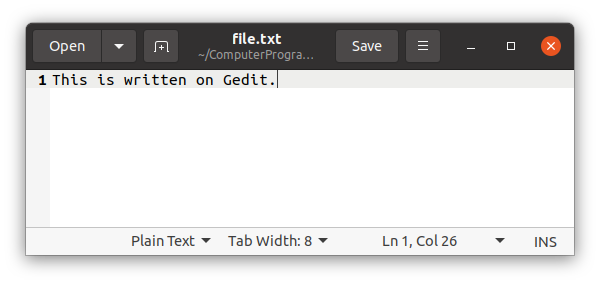
Then to close the text editor and back to the terminal window you can use ctrl+s to save, ctrl+w to close the document editing and once more ctrl+w to close Gedit. As an other way to close it, press ctrl+s to save and go back to the terminal and press ctrl+c.
Please note that we will not use Gedit to edit our files. We will use Vim which will be taught in the following lectures. This information is given here to write some files before learning Vim.
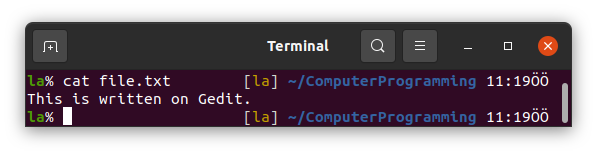
11. cat
You can write gedit file.txt to open the file again or you can use cat command to see what is in the file without leaving the terminal window.
We can also use cat to combine files. To do that first open another file as file2.txt using Gedit and write something in it. Save and exit.
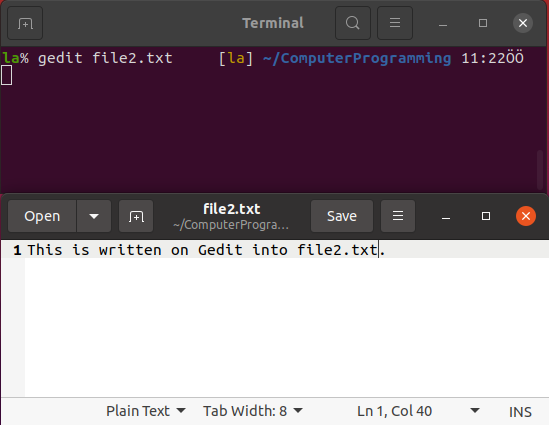
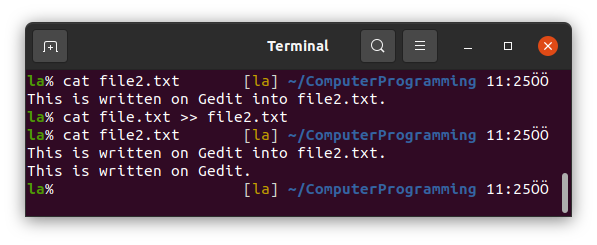
Now use cat to write what is included in file.txt into file2.txt and check it.
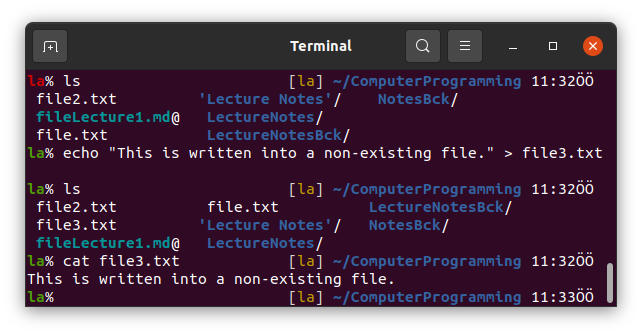
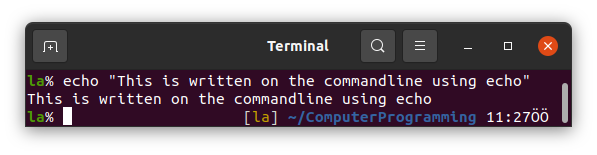
12. echo
We use echo to print anything on the command line.
We can also use echo to write something into a file. Try the following.
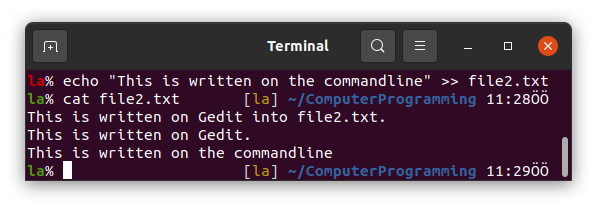
If the file does not exist, we should use single > instead of >>.